DNS Terminologies
- Domain Registrar: Amazon Route 53, GoDaddy,…
- DNS Records: A, AAAA, CNAME, NS,…
- Zone File: contains DNS records (Hostnames <-> IPs)
- Name Server: resolves DNS queries (Authoritative or Non-Authoritative)
- Top Level Domain (TLD): .com, .vn, .org,…
- Second Level Domain (SLD): google.com, amazon.com,…
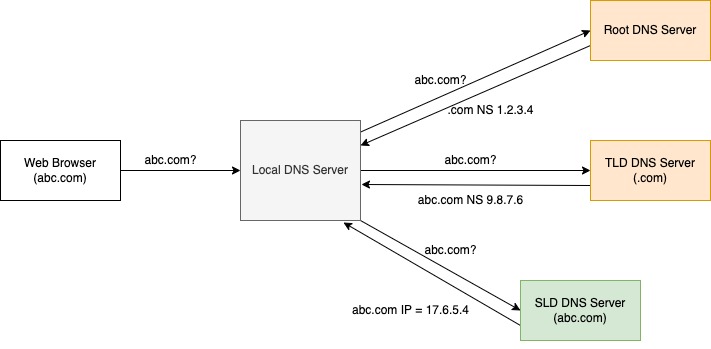
How it work
- User visit abc.com page in browser
- Web browser ask Local DNS Server (1) about abc.com
- If Local DNS Server already has seen this query before
-> return it to Web browser - If not, it ask the root DNS server (2)
- If the root DNS server know the answer
-> return it to Local DNS server - If not, it will return an IP of TLD DNS server (3) to Local DNS Server
- Local DNS Server will visit this IP to ask about abc.com
- If the TLD DNS server knows the answer
-> return it to Local DNS server - If not, it will return an IP of SLD DNS server (4) to Local DNS Server
- Local DNS Server will visit this IP to ask about abc.com
- SLD DNS server will return an IP address of abc.com
(1) Local DNS Server: assigned and managed by your company or assigned by your Internet Service Provider
(2) Root DNS server: is managed by ICANN organization
(3) TLD DNS server: is managed by IANA (Branch of ICANN)
(4) SLD DNS server: is managed by Domain Registrar (eg: Route53, GoDaddy,…)